
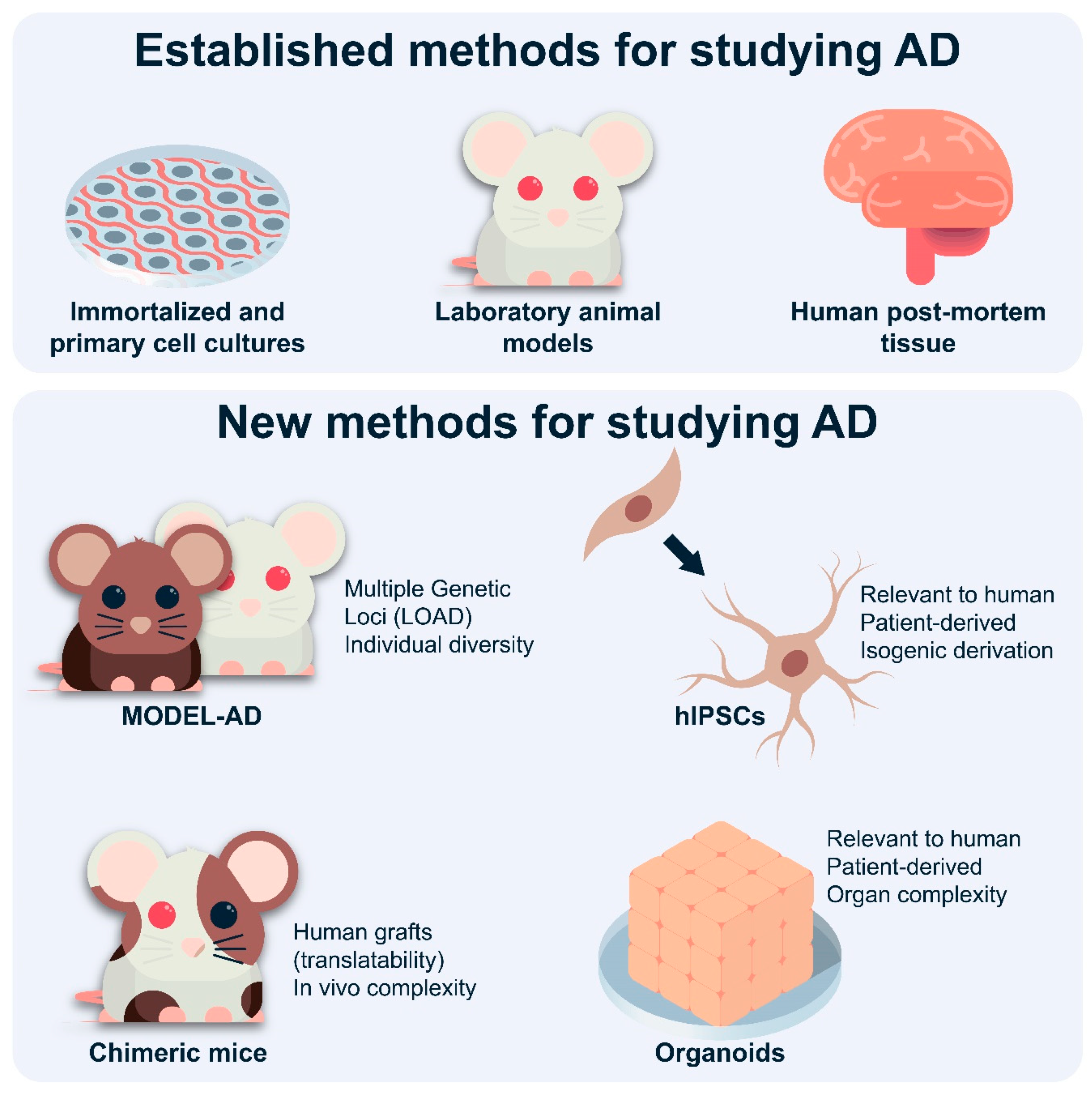
Stem Cell Therapies in Alzheimer's Disease: Applications for Disease Modeling | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics

Expression of ACAT1 in Alzheimer Disease mouse and cell models. (A) The... | Download Scientific Diagram
Cells | Free Full-Text | An Overview of Astrocyte Responses in Genetically Induced Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Models | HTML

Recent Expansions on Cellular Models to Uncover the Scientific Barriers Towards Drug Development for Alzheimer's Disease | SpringerLink
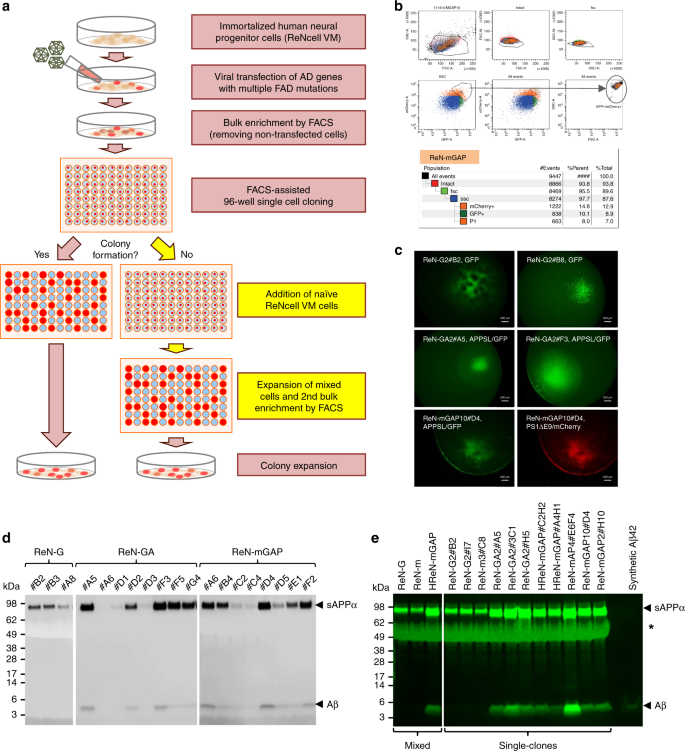
Amyloid-β42/40 ratio drives tau pathology in 3D human neural cell culture models of Alzheimer's disease | Nature Communications

miRNA-31 Improves Cognition and Abolishes Amyloid-β Pathology by Targeting APP and BACE1 in an Animal Model of Alzheimer's Disease - ScienceDirect

Counteracting the effects of TNF receptor‐1 has therapeutic potential in Alzheimer's disease | EMBO Molecular Medicine
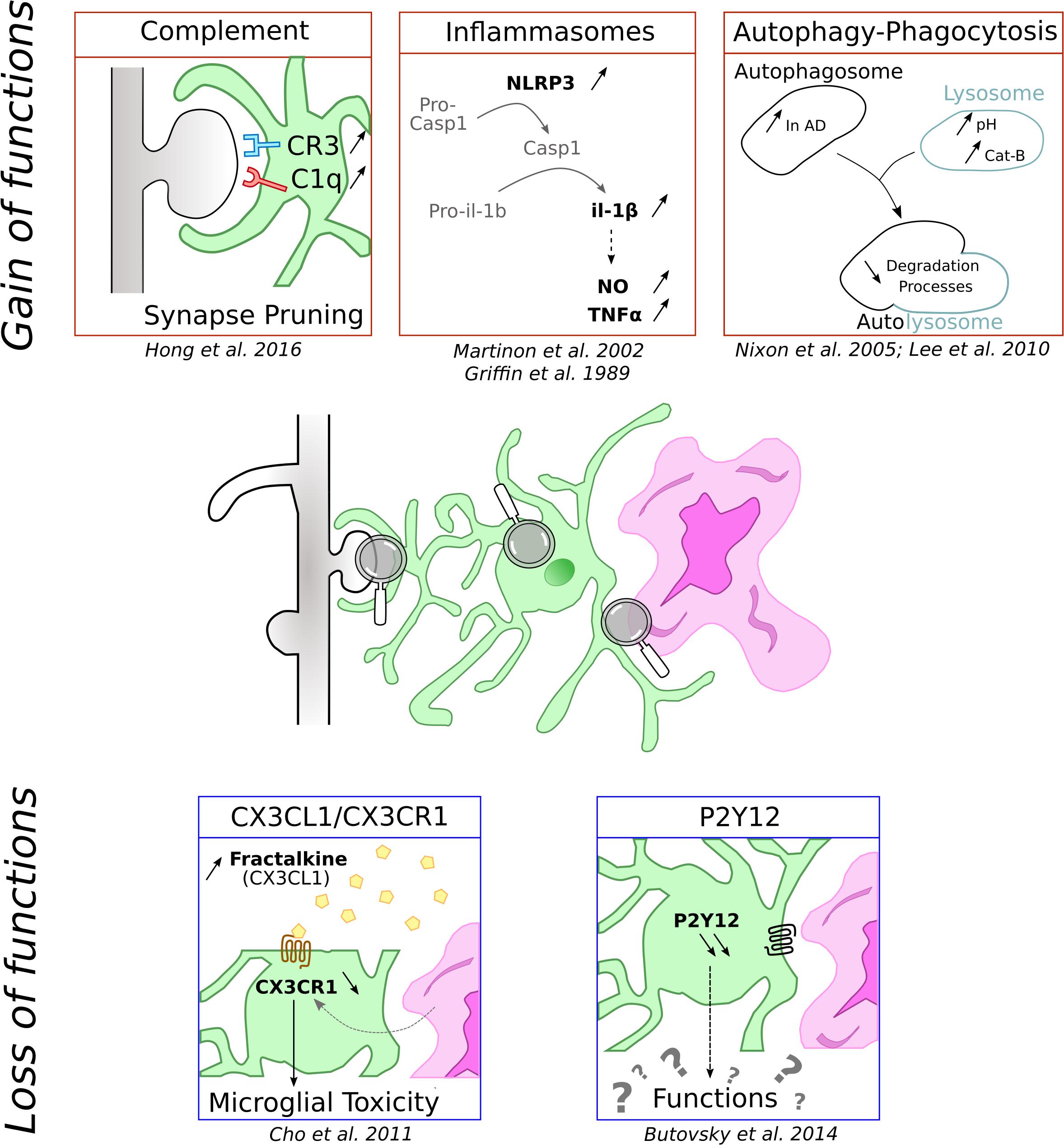
Frontiers | Microglia in Alzheimer Disease: Well-Known Targets and New Opportunities | Aging Neuroscience

Natural genetic variation determines microglia heterogeneity in wild-derived mouse models of Alzheimer's disease - ScienceDirect

Chronic deep brain stimulation in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model enhances memory and reduces pathological hallmarks - Brain Stimulation: Basic, Translational, and Clinical Research in Neuromodulation

BDNF-producing, amyloid β-specific CD4 T cells as targeted drug-delivery vehicles in Alzheimer's disease - eBioMedicine

Quantitative in vivo assessment of amyloid-beta phagocytic capacity in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model - ScienceDirect
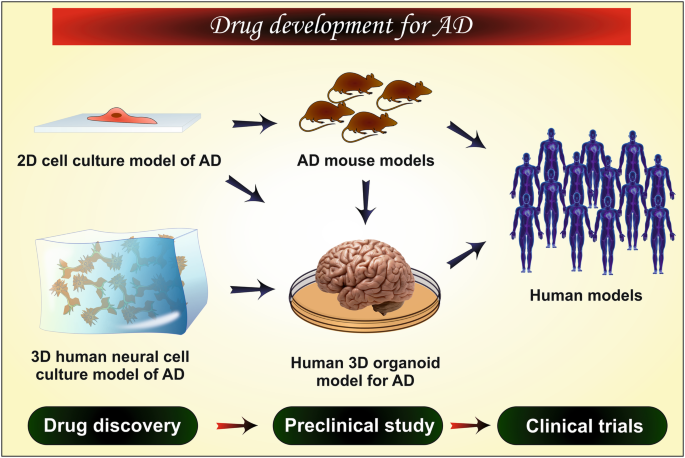
Recent Expansions on Cellular Models to Uncover the Scientific Barriers Towards Drug Development for Alzheimer's Disease | SpringerLink

In Vivo Chimeric Alzheimer's Disease Modeling of Apolipoprotein E4 Toxicity in Human Neurons - ScienceDirect

Schematic of the major animal models of Alzheimer's disease. Less than... | Download Scientific Diagram
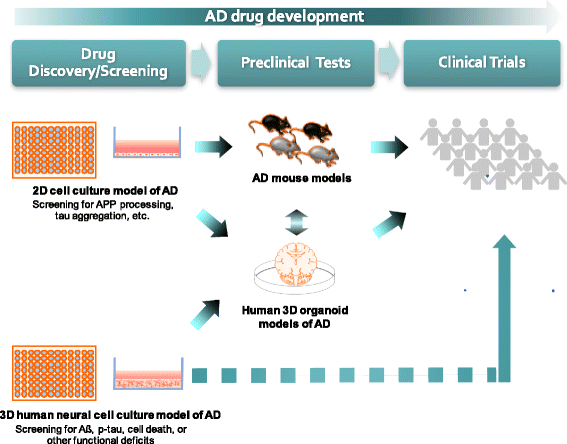
3D culture models of Alzheimer's disease: a road map to a “cure-in-a-dish” | Molecular Neurodegeneration | Full Text

Amyloid‐β oligomers in cellular models of Alzheimer's disease - Fontana - 2020 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library

Hallmarks of Alzheimer's Disease in Stem-Cell-Derived Human Neurons Transplanted into Mouse Brain: Neuron

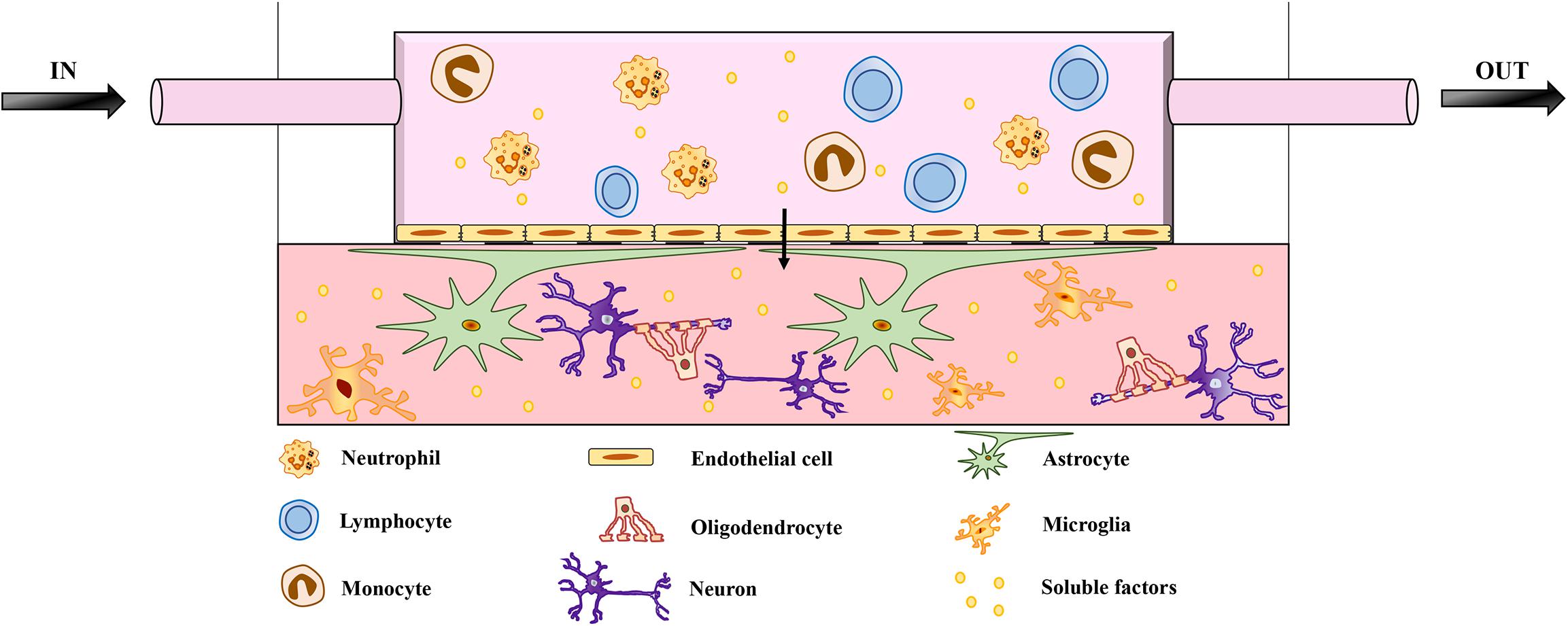


![PDF] Animal models of Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia | Semantic Scholar PDF] Animal models of Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/3001a2c4a156c34623702a97230e9f6aabaa4b4b/9-Figure4-1.png)

